Introduction
Shotgun proteomics using liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry (LC-MS) is commonly used to identify peptides containing post-translational modifications. With the emergence of fast database search tools such as MSFragger, the approach of enlarging precursor mass tolerances during the search (termed “open search”) has been increasingly used for comprehensive characterization of post-translational and chemical modifications of protein samples. However, not all mass shifts detected using the open search strategy represent true modifications, as artifacts exist from sources such as unaccounted missed cleavages or peptide co-fragmentation (chimeric MS/MS spectra). Here, we present Crystal-C, a computational tool that detects and removes such artifacts from open search results. Our analysis using Crystal-C shows that, in a typical shotgun proteomics data set, the number of such observations is relatively small. Nevertheless, removing these artifacts helps to simplify the interpretation of the mass shift histograms, which in turn should improve the ability of open search-based tools to detect potentially interesting mass shifts for follow-up investigation.
General Workflow
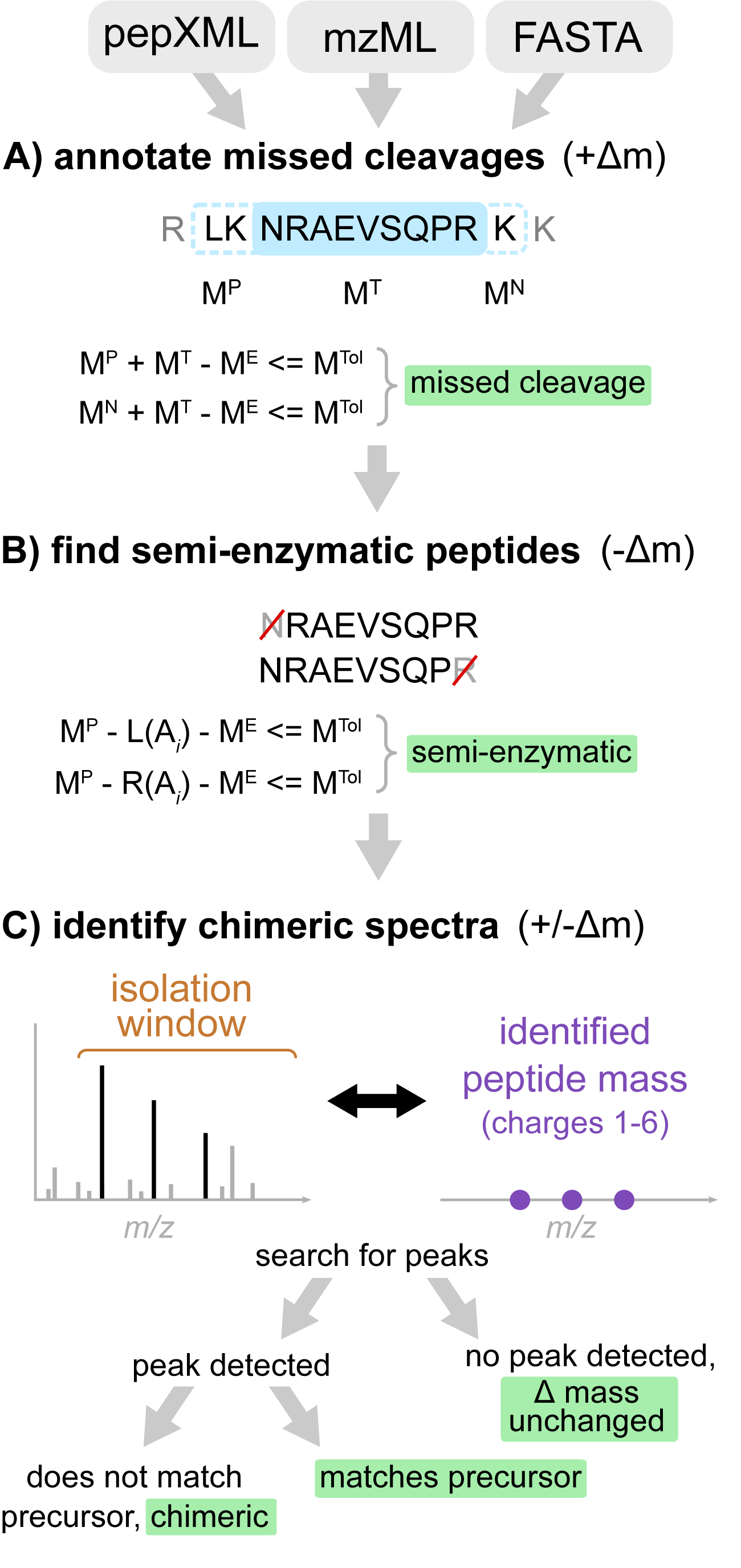
Figure. Workflow of Crystal-C as applied to each PSM from open search results. (A) Find potential missed cleavage sites by searching the previous and next fully enzymatic peptides of the identified peptide, where MTol is the mass tolerance (20 ppm by default), ME is the precursor neutral mass, MT is the identified peptide mass, and MP and MN are the previous and next adjacent fully enzymatic peptide masses, respectively. (B) Check whether the PSM is semi-enzymatic by deleting one amino acid from the left or right side of the identified peptide sequence at a time and calculating the mass difference between ME and the remaining peptide sequence. If the mass difference is smaller than MTol, the remaining peptide sequence is regarded as semi-enzymatic. (C) Find chimeric MS/MS spectra. Crystal-C searches for peaks from the identified peptide within the isolation window by comparing theoretical isotopic clusters (purple) to the MS1 spectrum. If a peak matching one of the theoretical isotope clusters is found in the isolation window and does not belong to the precursor, the PSM is considered chimeric.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| thread | Number of threads. “-1” means that Crystal-C automatically uses (total number of threads - 1) in your computer for processing. |
| fasta | Protein Fasta File |
| raw_file_location | The dictionary where the raw data locates |
| raw_file_extension | The file extension of raw data |
| output_location | The folder for the newly generated pepXML files |
| precursor_charge | The precursor charge state range |
| isotope_number | Number of theoretical isotope peaks need to be generated |
| precursor_mass | Precursor mass tolerance (unit: ppm) |
| precursor_isolation_window | Precursor Isolation Window (unit: Da.) |
| correct_isotope_error | Correct isotope error or not |
How to Download
Download the latest version here
How to Cite
Chang HY, Kong AT, da Veiga Leprevost F, Avtonomov DM, Haynes SE, Nesvizhskii AI. Crystal-C: A Computational Tool for Refinement of Open Search Results. J Proteome Res. 2020. Manuscript
For other tools developed by the Nesvizhskii lab, see our website: www.nesvilab.org.
Commands
(for mzML files)
java -Xmx53G -cp "CrystalC-1.2.1.jar" crystalc.Run crystalc.params *.pepXML
(for Thermo RAW files)
java -Dbatmass.io.libs.thermo.dir="D:\MSFragger-3.0\ext\thermo" -Xmx53G -cp "CrystalC-1.2.1.jar" crystalc.Run crystalc.params *.pepXML